One of the rarest autoimmune diseases, Still’s disease can strike adults and children alike. Doctors and patients alike are frequently confused by its unpredictable nature, which is characterized by high fevers, joint pain, and a characteristic rash. However, those who suffer from this complicated illness have hope thanks to advancements in treatment.
The Reasons Still’s Disease Is Frequently Misdiagnosed
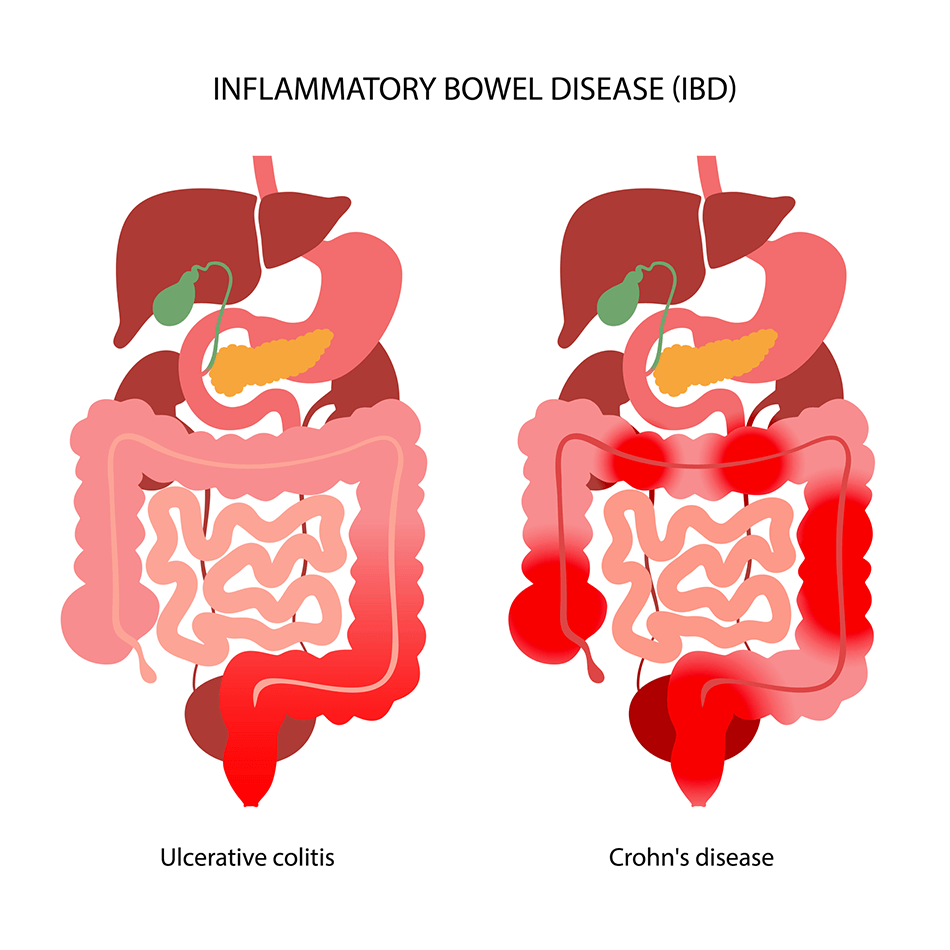
Still’s disease symptoms are remarkably similar to those of other infectious and inflammatory diseases. Because of this, diagnosis is very challenging. Elevated serum ferritin levels are frequently a key indicator that doctors must carefully rule out other possibilities.
Key Insights on Still’s Disease
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Disease Name | Still’s Disease (Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis & Adult-Onset Still’s Disease) |
| Symptoms | High fevers, joint pain, sore throat, salmon-colored rash, muscle pain |
| Diagnosis | Clinical evaluation, blood tests (ferritin, inflammatory markers), imaging scans |
| Treatment Options | NSAIDs, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, biologics (Anakinra, Tocilizumab) |
| Specialists Involved | Rheumatologists, immunologists, internal medicine doctors |
| Related Conditions | Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, macrophage activation syndrome |
| Prognosis | Varies from mild, episodic cases to severe, chronic joint damage |
Identifying Still’s Disease’s Early Symptoms
Rashes and spiking fevers are examples of symptoms that could be mistaken for a common viral illness, delaying diagnosis. Joint stiffness and pain get worse over time, and if treatment is not received, some patients may suffer long-term harm.
The Way the Immune System Activates
Chronic inflammation results from an aggressive immune response brought on by Still’s disease. Increased levels of interleukin-1 and interleukin-6, two important proteins that promote inflammation and play a role in the disease’s periodic flare-ups, have been connected by researchers to this.
The Distinction Between Adult-Onset and Juvenile Still’s Disease
Children can develop systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA), whereas adults over 16 can develop adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD). Although the underlying inflammation in both conditions is the same, AOSD can be more severe and occasionally necessitate lifelong care.
Advances in the Management of Still’s Disease
The cornerstone of treatment has been conventional therapies like corticosteroids and NSAIDs. However, patients now enjoy a much higher quality of life thanks to the introduction of biologics like Anakinra and Tocilizumab, which have significantly improved disease control.
The Silent Danger: When Still’s Illness Turns Into a Life-Threatening Situation
A rare but serious complication where the immune system goes haywire is macrophage activation syndrome (MAS). Early detection and intervention are especially important because MAS can result in organ failure if treatment is not received.
Managing Still’s Disease in Daily Life
Having Still’s disease is a constant struggle that needs to be carefully managed. To preserve mobility and general well-being, patients frequently follow an anti-inflammatory diet, closely monitor their symptoms, and continue to be physically active.
Are You Ignoring Still’s Disease?
Although Still’s disease is uncommon, its symptoms can appear surprisingly widespread. Seeking the advice of a rheumatologist can be transformative if chronic fevers, inexplicable rashes, and joint pain interfere with day-to-day functioning. The key to avoiding complications is early treatment.
The Prospects for Research on Still’s Disease
For patients with Still’s disease, exciting advances in biologic therapies and personalized medicine are changing the game. Scientists are using state-of-the-art research to find new ways to control inflammation and enhance long-term results.